Search algorithms
Structured data
More emphasis on the "new" SEO trends
1. New Page Experience indicators will affect rankings
2. Mobile indexing will be the main driver for all websites
3. Artificial Intelligence(AI) will dominate all searches
4. Entities will be used as equivalent to back links
5. EAT factors are given a greater role
6. Local SEO is becoming increasingly complex
7. Structured data is becoming inevitable
8. Google will make more effort to satisfy search intent
New user experience indicators will affect rankings
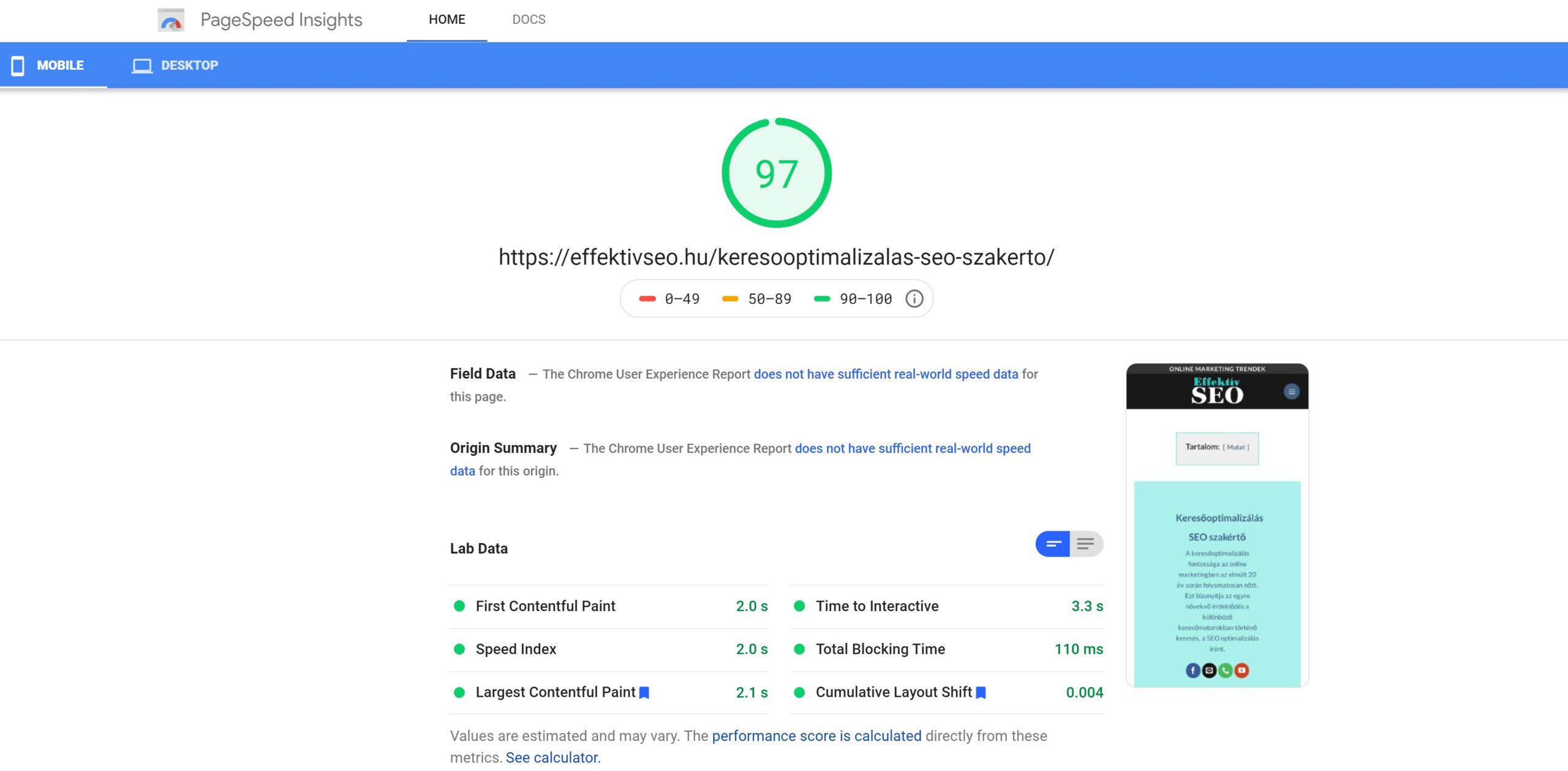
Page Speed Insights Google
Mobile
When this happens, these indicators will be used as tie-breakers rather than strong ranking factors. So, for example, if there are two sites with the same content, similar quality and Authority, it will be up to the user experience metrics to decide which one to rank higher.
In addition, Core Web Vitals serves as a qualifier for sites that want to appear in Google Top Stories. Previously, only AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) sites could appear in Top Stories because they were reliably fast. Now that Google can measure speed using Core Web Vitals, this option is extended to all pages with a high enough optimization score.
In addition, Google is considering some kind of identifier to tag search results with a good user experience. Similar to the way AMP pages are marked with a lightning bolt icon. If implemented, users may find fast pages in search results and are likely to prefer them to slow pages. How to optimise Core Web Vitals can be measured using any number of tools from Google Web Developers: PageSpeed Insights, Chrome UX Report, Search Console, Chrome DevTools, Lighthouse and Web Vitals Chrome Extension. Most of these tools also give you suggestions on how to improve each metric, so you just need to follow the advice until you get the values you want.
Mobile indexing will be the default for all websites
Artificial intelligence will dominate all searches

Artificial intelligence
BERT
Bert is a natural language processing, an approach that can be used on large amounts of text. It handles tasks such as entity recognition, part of speech tagging and question answering, among other natural language processes. Bert helps Google understand natural language texts on the web. Google has open sourced this technology and others have created variations of BERT.
Entities will be used as equivalent to backlinks
EAT (Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness) factors may play a greater role
Local SEO is becoming increasingly complex

Local SEO
Google My Business
Structured data is becoming inevitable
Structured data
Local search results

